Dog Internal Anatomy - Dog anatomy is how a dog is built.
Dog Internal Anatomy - Details of structures vary tremendously from breed to breed, more than in any other animal species, wild or domesticated, [1] as dogs are highly variable in height and weight. Responsible for circulating blood and delivering oxygen and nutrients to the body’s tissues. Dogs, like humans, have a complex system of internal organs that work together to keep them healthy and functioning. The following paragraphs explain all these aspects in brief, along with diagrams, which will help you understand them better. We will be covering the most commonly used body parts of a dog, including the abdomen, throat, back, nape, belly, brisket, wrist, chest, prosternum, croup, claw, ear, elbow, and many more.
Their bodies are made up of many different parts, including their skeleton, muscles and internal organs. Canine anatomy is a complex and fascinating subject that encompasses the structure and function of a dog’s body. Our aim is to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the different parts of a dog’s anatomy. The cerebrum is the part of the dog's brain which performs functions such as learning. Within a dog’s skull lies the brain, the control center of their body. Hill’s atlas of veterinary clinical anatomy. Muscle, organ and skeletal anatomy).
Dog Internal Organs Anatomy Anatomy Of A Male Dog Internal Org Stock
The axial skeleton (skull, spine, and ribs) and the appendicular skeleton (limbs and girdles). In this article, you will learn the location of different organs from the different systems (like skeletal, digestive, respiratory, urinary, cardiovascular, endocrine, nervous, and special sense) of a dog with their important anatomical features. Helped over 8mm worldwide12mm+ questions answered Dog.
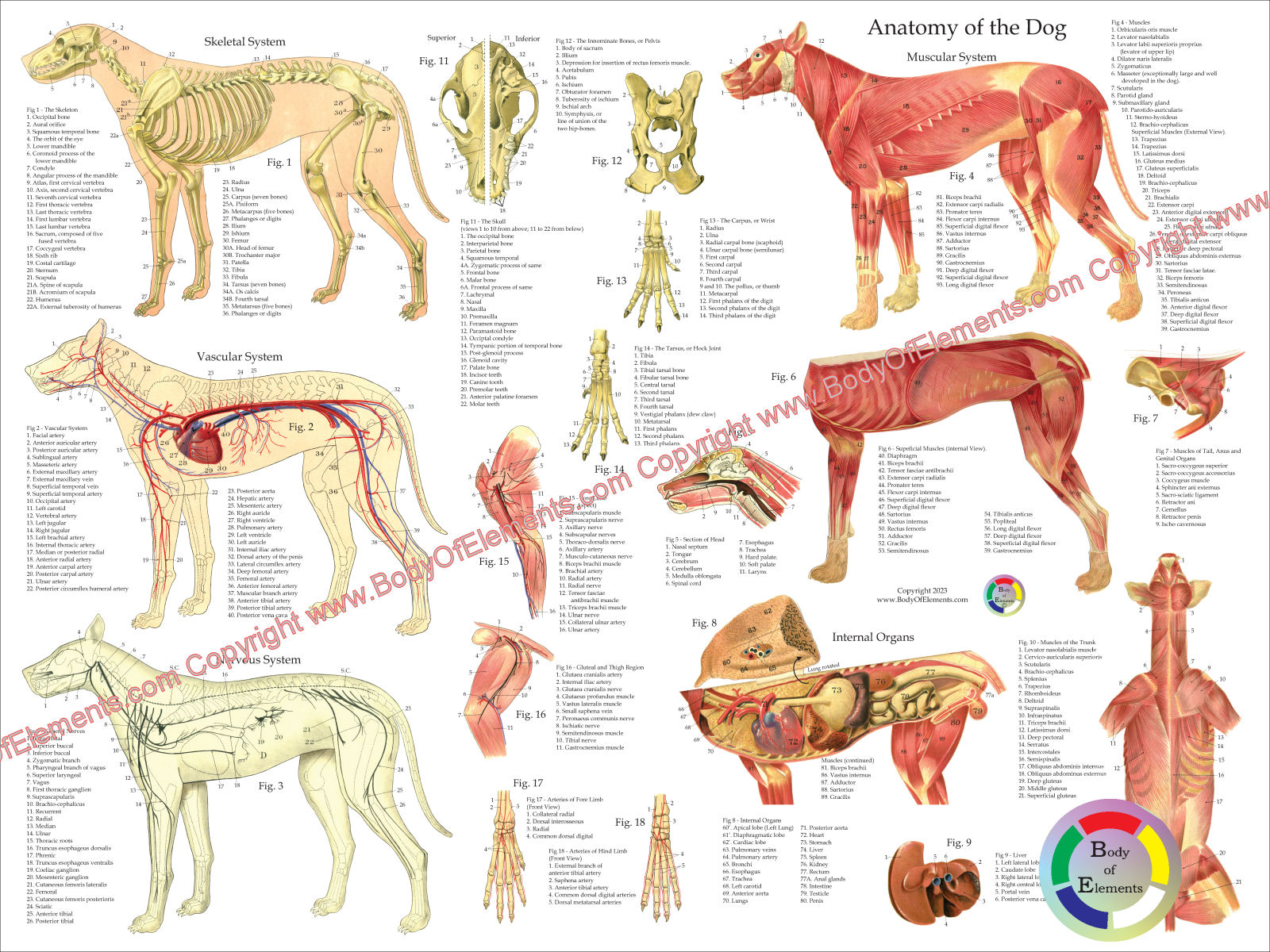
Dog Anatomy Poster
Dogs, like humans, have a complex system of internal organs that work together to keep them healthy and functioning. A dog's physical anatomy is designed to help them navigate their environment and perform various tasks. Dog anatomy comprises the anatomical study of the visible parts of the body of a domestic dog. Labeled images in.
Canine Internal Anatomy Chart. Anatomy of Dog with Inside Organ
Here are presented scientific illustrations of the canine muscles and skeleton from different anatomical standard views (lateral, medial, cranial, caudal, dorsal, ventral / palmar.). Dog anatomy details the various structures of canines (e.g. The cerebrum is the part of the dog's brain which performs functions such as learning. Some of the different canine joints are.
Dog Internal Organs Anatomy Anatomy of a Male Dog Internal Org Stock
• the sagittal plane divides the dog into right and left portions. Positional and directional terms, general terminology and anatomical orientation are. The internal anatomy of dogs, is very similar to the anatomy of other carnivorous mammals such as the cat. The skull not only protects this vital organ but also plays a role in.
Внутренние органы собаки. Вид справа Dog Internal Organs, Anatomy
• the sagittal plane divides the dog into right and left portions. The anatomy of a dog includes its skeletal structure, reproductive system, the internal organs, and its external appearance. The skull not only protects this vital organ but also plays a role in determining a dog’s overall appearance and specific breed characteristics. You can.
Dog Internal Anatomy Anatomical Charts & Posters
The detailing of these structures changes based on dog breed due to the huge variation of size in dog breeds. Fully labeled illustrations and diagrams of the dog (skeleton, bones, muscles, joints, viscera, respiratory system, cardiovascular system). Exploring the internal organs of a dog. Canine anatomy is a complex and fascinating subject that encompasses the.
Dog Internal Anatomy Poster 24 x 36
On the left side view of a dog's internal organs, you can see the lungs, heart, liver, stomach, spleen, kidney, intestines, bladder, and the rectum in that order from front to back. Each body part plays an important role in how. The detailing of these structures changes based on dog breed due to the huge.
Poster organe interne caine Tuvet
Anatomy atlas of the canine general anatomy: Just like humans, dogs’ bones are composed of calcium and collagen, providing strength and flexibility. Their bodies are made up of many different parts, including their skeleton, muscles and internal organs. The cerebrum is the part of the dog's brain which performs functions such as learning. Dog anatomy.
Dog Internal Anatomy Poster Dog anatomy, Anatomy, Dogs
We will be covering the most commonly used body parts of a dog, including the abdomen, throat, back, nape, belly, brisket, wrist, chest, prosternum, croup, claw, ear, elbow, and many more. The following paragraphs explain all these aspects in brief, along with diagrams, which will help you understand them better. Here are presented scientific illustrations.
Dog Digestive Process and what the stages are and how it works
• the sagittal plane divides the dog into right and left portions. In this article, you will learn the location of different organs from the different systems (like skeletal, digestive, respiratory, urinary, cardiovascular, endocrine, nervous, and special sense) of a dog with their important anatomical features. Responsible for circulating blood and delivering oxygen and nutrients.
Dog Internal Anatomy The axial skeleton (skull, spine, and ribs) and the appendicular skeleton (limbs and girdles). Exploring the internal organs of a dog. Canine anatomy is a complex and fascinating subject that encompasses the structure and function of a dog’s body. The outer ear includes the pinna (the part you see that is made of cartilage and covered by skin, fur, or hair) and the ear canal. In this article, you will learn the location of different organs from the different systems (like skeletal, digestive, respiratory, urinary, cardiovascular, endocrine, nervous, and special sense) of a dog with their important anatomical features.
Our Aim Is To Provide You With A Comprehensive Understanding Of The Different Parts Of A Dog’s Anatomy.
One of the most important parts of a. • the dorsal plane divides the dog into ventral and dorsal portions. Canine anatomy is a complex and fascinating subject that encompasses the structure and function of a dog’s body. Helped over 8mm worldwide12mm+ questions answered
It Consists Of The Outer, Middle, And Inner Ear.
The internal anatomy of dogs, is very similar to the anatomy of other carnivorous mammals such as the cat. A dog's physical anatomy is designed to help them navigate their environment and perform various tasks. The cerebrum is the part of the dog's brain which performs functions such as learning. The skeletal system of dogs is divided into two main parts:
Dog Anatomy Is How A Dog Is Built.
The following paragraphs explain all these aspects in brief, along with diagrams, which will help you understand them better. In dogs, the pinnae are mobile and can move independently of each other. The axial skeleton (skull, spine, and ribs) and the appendicular skeleton (limbs and girdles). Dog anatomy organs left side.
Here Are Presented Scientific Illustrations Of The Canine Skeleton, With The Main Dog's Bones And Its Structures Displayed From Different Anatomical Standard Views (Cranial, Caudal, Lateral, Medial, Dorsal, Palmar.).
We will be covering the most commonly used body parts of a dog, including the abdomen, throat, back, nape, belly, brisket, wrist, chest, prosternum, croup, claw, ear, elbow, and many more. Dog anatomy comprises the anatomical study of the visible parts of the body of a domestic dog. Some of the different canine joints are labeled. The outer ear includes the pinna (the part you see that is made of cartilage and covered by skin, fur, or hair) and the ear canal.