Shoulder X Ray Anatomy - The bones, the joints and soft tissue.
Shoulder X Ray Anatomy - The acromion and the coracoid process could be visualized as the index finger and thumb respectively, always pointing towards anterior (fig. The shoulder series is fundamentally composed of two orthogonal views of the glenohumeral joint including the entire scapula. The extension of the shoulder series depends on the radiography department protocols and the clinical indications for imaging. External rotation views and internal rotation views from two different patients. Compare the glenohumeral joint with a golf ball (humeral head) and a tee (glenoid).
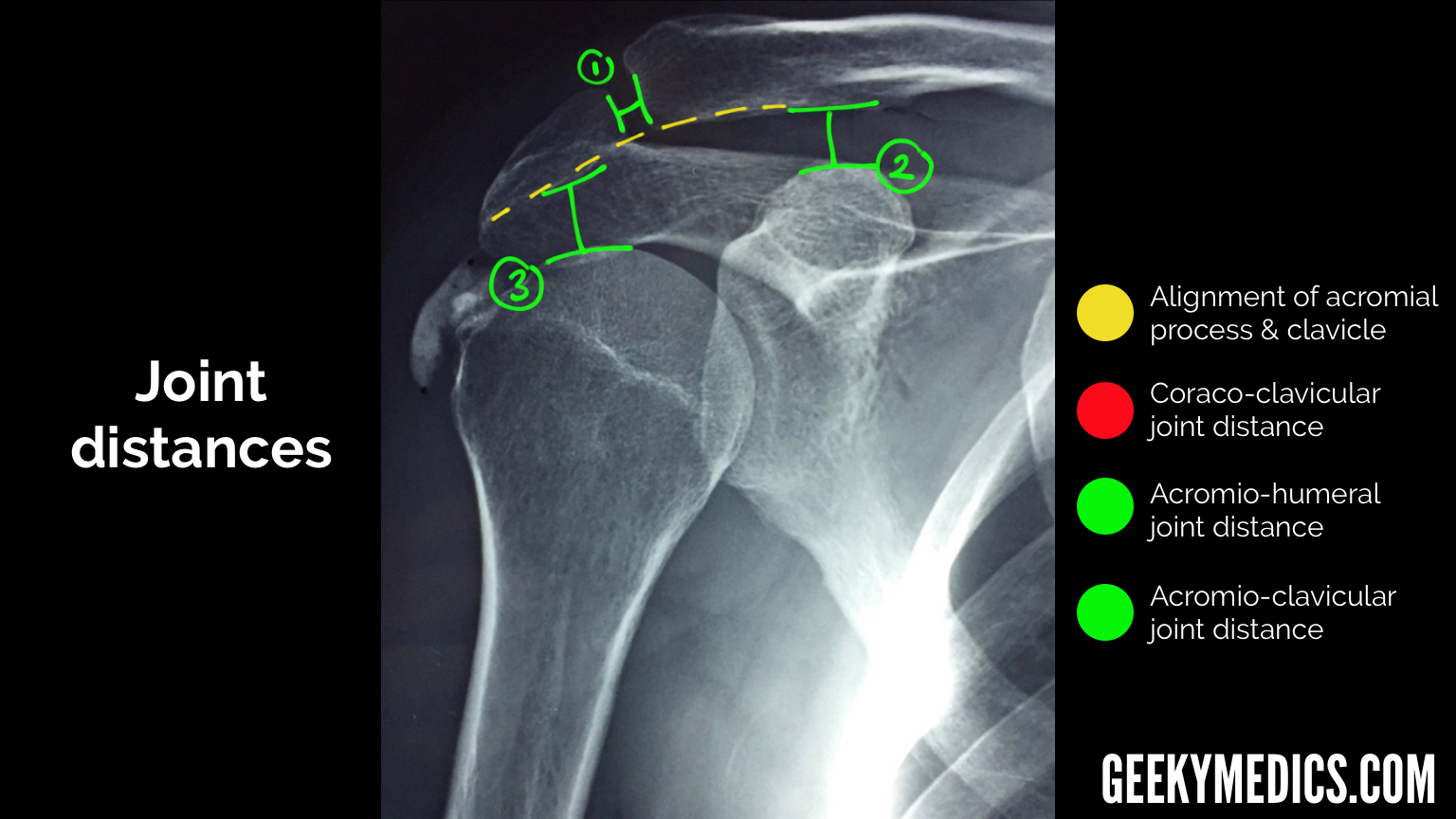
Some of the key topics are proximal humeral fracture, shoulder dislocation, bankart lesion and osteoarthritis. A recommended systematic checklist for reviewing musculoskeletal exams is: Comprising numerous ligamentous and muscular structures, the only actual bony articulations are the glenohumeral joint and the acromioclavicular joint (acj). The bones of the shoulder include the proximal humerus, the lateral clavicle, the ribs, and the scapula. The glenoid fossa is perpendicular to the body of the scapula. The scapula is, in turn, subdivided into the glenoid, the coracoid, and the acromion. The projection demonstrates the shoulder in its natural anatomical position allowing for adequate radiographic examination of the entire clavicle and scapula, as well as the glenohumeral, acromioclavicular and sternoclavicular joints of the shoulder girdle.
Xray of shoulder joint. Irvings Law
Comprising numerous ligamentous and muscular structures, the only actual bony articulations are the glenohumeral joint and the acromioclavicular joint (acj). The scapula is, in turn, subdivided into the glenoid, the coracoid, and the acromion. External rotation views and internal rotation views from two different patients. We see the scapula or shoulder blade. Lateral view 1.
Anatomy of Shoulder Xrays YouTube
Third most common musculoskeletal complaint, second only to low back pain and neck pain [3] 43 public playlists include this case. The glenoid fossa is perpendicular to the body of the scapula. The bones of the shoulder include the proximal humerus, the lateral clavicle, the ribs, and the scapula. The acromion and the coracoid process.
Intertubercular Groove Xray
Comprising numerous ligamentous and muscular structures, the only actual bony articulations are the glenohumeral joint and the acromioclavicular joint (acj). The glenoid fossa is perpendicular to the body of the scapula. Shoulder girdle , radiographs : A recommended systematic checklist for reviewing musculoskeletal exams is: The projection demonstrates the shoulder in its natural anatomical position.
AP of the shoulder Medical anatomy, Radiology student, Radiology schools
It details the bones, joints, ligaments, tendons, and muscles of the shoulder and describes normal anatomy as well as common variants and injuries seen on imaging. The coracoid process is seen projecting above the clavicle. Third most common musculoskeletal complaint, second only to low back pain and neck pain [3] The bones of the shoulder.
UCSD Musculoskeletal Radiology
The bones, the joints and soft tissue. The bones of the shoulder include the proximal humerus, the lateral clavicle, the ribs, and the scapula. The shoulder series is fundamentally composed of two orthogonal views of the glenohumeral joint including the entire scapula. Why the shoulder matters and the radiology rule of 2’s. There for optimal.
Scapula Anatomy Xray
External rotation views and internal rotation views from two different patients. The images above outline the normal osseous anatomy in red. 3 articles feature images from this case. We see the glenoid or socket of the shoulder joint. The bones, the joints and soft tissue. A recommended systematic checklist for reviewing musculoskeletal exams is: The.
Scapula Anatomy Xray
Some of the key topics are proximal humeral fracture, shoulder dislocation, bankart lesion and osteoarthritis. The shoulder, or shoulder joint, is the connection between the upper arm and the thorax. The osseous glenoid fossa is markedly smaller than the humeral head (ratio about 1:4) according to bigliani (1982), three different acromial types can be observed.
Shoulder xrays image stock image. Image of body, humerus 27604697
3 articles feature images from this case. Axillary superoinferior position allows optimum imaging of joint space between the humeral head and the glenoid. 4 articles feature images from this case. The projection demonstrates the shoulder in its natural anatomical position allowing for adequate radiographic examination of the entire clavicle and scapula, as well as the.
Shoulder Xray Interpretation Radiology Geeky Medics
The coracoid process is seen projecting above the clavicle. The bones, the joints and soft tissue. The shoulder, or shoulder joint, is the connection between the upper arm and the thorax. 4 articles feature images from this case. Third most common musculoskeletal complaint, second only to low back pain and neck pain [3] The projection.
Anteroposterior radiograph of the right shoulder The BMJ
4 articles feature images from this case. Why the shoulder matters and the radiology rule of 2’s. Review the entire radiograph,regardless of perceived difficulty. 3 articles feature images from this case. The projection demonstrates the shoulder in its natural anatomical position allowing for adequate radiographic examination of the entire clavicle and scapula, as well as.
Shoulder X Ray Anatomy Lateral view 1 coracoid process. Click image to see overlay. The glenoid fossa is perpendicular to the body of the scapula. The osseous glenoid fossa is markedly smaller than the humeral head (ratio about 1:4) according to bigliani (1982), three different acromial types can be observed in the coronal plane: There are three main components of the shoulder radiography:
External Rotation Views And Internal Rotation Views From Two Different Patients.
The bones, the joints and soft tissue. A recommended systematic checklist for reviewing musculoskeletal exams is: The normal osseous anatomy is outlined. Lateral view 1 coracoid process.
We See The Glenoid Or Socket Of The Shoulder Joint.
The projection demonstrates the shoulder in its natural anatomical position allowing for adequate radiographic examination of the entire clavicle and scapula, as well as the glenohumeral, acromioclavicular and sternoclavicular joints of the shoulder girdle. Why the shoulder matters and the radiology rule of 2’s. The glenoid fossa is perpendicular to the body of the scapula. The upper part of the lung and ribs are also seen.
Some Of The Key Topics Are Proximal Humeral Fracture, Shoulder Dislocation, Bankart Lesion And Osteoarthritis.
It is helpful for detecting the anterior and posterior glenohumeral dislocations. The shoulder internal rotation view is an additional projection to the standard shoulder series it is often combined with the external rotation view to visualize the entirety of the humeral head. Scroll or drag your finger down to reveal the radiographic anatomy for each shoulder view. 4 articles feature images from this case.
The Coracoid Process Is Seen Projecting Above The Clavicle.
Magnification artifacts that are associated with radiographs do not occur with ct. It details the bones, joints, ligaments, tendons, and muscles of the shoulder and describes normal anatomy as well as common variants and injuries seen on imaging. The shoulder series is fundamentally composed of two orthogonal views of the glenohumeral joint including the entire scapula. Provides better detail of cortical and trabecular bone structures than mri at cost of higher radiation exposure.