Mandible Anatomy Radiology - Anatomy the mandible is the only freely movable bone of the face;
Mandible Anatomy Radiology - Mdct, cbvct, and mri are used for the advanced imaging of the mandible and facial region (table 4.1). The mandible is the largest bone in the human skull, has a parabolic shape, houses the lower teeth, and articulates with the maxillary teeth and temporal bone. The mandible is the largest and strongest facial bone which can preserve its shape better than any other bone in the forensic and anthropologic field. This pictorial essay depicts normal gross andct anatomy ofthemandible andpresents aseries ofcases that illustrate theutility ofctinexamining mandibular lesions. The axiolateral oblique mandible view allows for visualization of the mandibular body, mandibular ramus, condylar process and mentum.
It articulates with the temporal bone in the temporomandibular fossa anterior to the external auditory canal (see fig. Anatomy the mandible is the only freely movable bone of the face; The mandible is the single midline bone of the lower jaw. Articulation with the skull base at the bilateral temporomandibular joints allows a range of movements facilitated by associated muscles, including dental occlusion with the maxilla. The range of motion is free in all directions, and the condyle moves downward and forward in the articular fossa upon opening of the jaw. This pictorial essay depicts normal gross andct anatomy ofthemandible andpresents aseries ofcases that illustrate theutility ofctinexamining mandibular lesions. The mandible is the largest and strongest facial bone which can preserve its shape better than any other bone in the forensic and anthropologic field.
Technology and Techniques in Radiology Mandible Radiographic Anatomy
Mandibular fractures are relatively common especially among young men. Although traditionally the mandible and base of skull are thought to form a complete bony ring, interrupted only by the tmjs. This pictorial essay depicts normal gross andct anatomy ofthemandible andpresents aseries ofcases that illustrate theutility ofctinexamining mandibular lesions. Although the oral cavity poses particular complexity.
soft tissue anatomy in mandible view Dental hygiene student
The mandible is the single midline bone of the lower jaw. Although the oral cavity poses particular complexity in head and neck imaging, a sound understanding of radiological anatomy, common pathways of disease spread and current complementary technical approaches will improve detection and characterisation of. The axiolateral oblique mandible view allows for visualization of the.
RxDentistry Radiographic Anatomy of Facial Bones
The mandible is also the insertion point for a range of muscles involved in facial expression. Mandibular fractures are relatively common especially among young men. Although the oral cavity poses particular complexity in head and neck imaging, a sound understanding of radiological anatomy, common pathways of disease spread and current complementary technical approaches will improve.
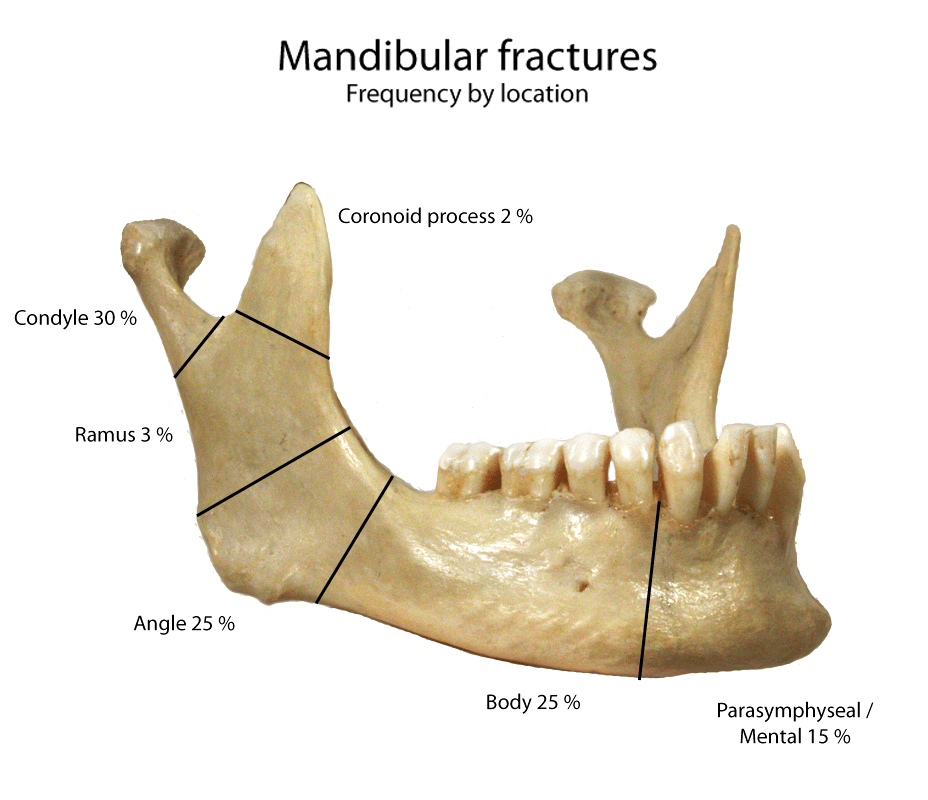
Mandibular Fractures Anatomy, Management Geeky Medics
The axiolateral oblique mandible view allows for visualization of the mandibular body, mandibular ramus, condylar process and mentum. The mandible is the largest and strongest facial bone which can preserve its shape better than any other bone in the forensic and anthropologic field. The mandible is also the insertion point for a range of muscles.
Mandible xrays
Articulation with the skull base at the bilateral temporomandibular joints allows a range of movements facilitated by associated muscles, including dental occlusion with the maxilla. Mandibular fractures are relatively common especially among young men. The mandible is also the insertion point for a range of muscles involved in facial expression. This pictorial essay depicts normal.
Image
The mandible is the largest bone in the human skull, has a parabolic shape, houses the lower teeth, and articulates with the maxillary teeth and temporal bone. This pictorial essay depicts normal gross andct anatomy ofthemandible andpresents aseries ofcases that illustrate theutility ofctinexamining mandibular lesions. The mandible is utilized to distinguish between the ethnic groups.
Multidetector CT of Mandibular Fractures, Reductions, and Complications
The range of motion is free in all directions, and the condyle moves downward and forward in the articular fossa upon opening of the jaw. This pictorial essay depicts normal gross andct anatomy ofthemandible andpresents aseries ofcases that illustrate theutility ofctinexamining mandibular lesions. It articulates with the temporal bone in the temporomandibular fossa anterior to.
Dentistry lectures for MFDS/MJDF/NBDE/ORE Radiographic Anatomy of
The mandible is the single midline bone of the lower jaw. Mandibular fractures are relatively common especially among young men. Mdct, cbvct, and mri are used for the advanced imaging of the mandible and facial region (table 4.1). The mandible is utilized to distinguish between the ethnic groups and sexes [ 1 ]. Although traditionally.
Mandible Radiographic Anatomy wikiRadiography
It articulates with the temporal bone in the temporomandibular fossa anterior to the external auditory canal (see fig. Plain films including panoramic and intraoral dental images remain a standard starting point for the study of the body of the mandible, dentoalveolar processes, and teeth. The mandible is the largest bone in the human skull, has.
Radiopaedia Drawing Inferior alveolar nerve of mandibular nerve
Mdct, cbvct, and mri are used for the advanced imaging of the mandible and facial region (table 4.1). This pictorial essay depicts normal gross andct anatomy ofthemandible andpresents aseries ofcases that illustrate theutility ofctinexamining mandibular lesions. It consists of a curved, horizontal portion, the body, and two perpendicular portions, the rami, which unite with the.
Mandible Anatomy Radiology Plain films including panoramic and intraoral dental images remain a standard starting point for the study of the body of the mandible, dentoalveolar processes, and teeth. The mandible is also the insertion point for a range of muscles involved in facial expression. The mandible is the single midline bone of the lower jaw. The mandible is the largest bone in the human skull, has a parabolic shape, houses the lower teeth, and articulates with the maxillary teeth and temporal bone. Although traditionally the mandible and base of skull are thought to form a complete bony ring, interrupted only by the tmjs.
The Mandible Is Utilized To Distinguish Between The Ethnic Groups And Sexes [ 1 ].
The mandible is the largest bone in the human skull, has a parabolic shape, houses the lower teeth, and articulates with the maxillary teeth and temporal bone. Articulation with the skull base at the bilateral temporomandibular joints allows a range of movements facilitated by associated muscles, including dental occlusion with the maxilla. The mandible is also the insertion point for a range of muscles involved in facial expression. Anatomy the mandible is the only freely movable bone of the face;
The Mandible Is The Single Midline Bone Of The Lower Jaw.
Plain films including panoramic and intraoral dental images remain a standard starting point for the study of the body of the mandible, dentoalveolar processes, and teeth. It consists of a curved, horizontal portion, the body, and two perpendicular portions, the rami, which unite with the ends of the body nearly at right angles (angle of the jaw). It articulates with the temporal bone in the temporomandibular fossa anterior to the external auditory canal (see fig. The axiolateral oblique mandible view allows for visualization of the mandibular body, mandibular ramus, condylar process and mentum.
Mdct, Cbvct, And Mri Are Used For The Advanced Imaging Of The Mandible And Facial Region (Table 4.1).
Mandibular fractures are relatively common especially among young men. This pictorial essay depicts normal gross andct anatomy ofthemandible andpresents aseries ofcases that illustrate theutility ofctinexamining mandibular lesions. The range of motion is free in all directions, and the condyle moves downward and forward in the articular fossa upon opening of the jaw. Although the oral cavity poses particular complexity in head and neck imaging, a sound understanding of radiological anatomy, common pathways of disease spread and current complementary technical approaches will improve detection and characterisation of.
The Mandible Is The Largest And Strongest Facial Bone Which Can Preserve Its Shape Better Than Any Other Bone In The Forensic And Anthropologic Field.
Although traditionally the mandible and base of skull are thought to form a complete bony ring, interrupted only by the tmjs.









.jpg)