Male Snake Anatomy - Male snakes and their hemipenes • snake hemipenes revealed • discover the unique anatomy of male snakes and learn about their paired.
Male Snake Anatomy - These are essentially the equivalent of two small penises. Snake repellents — how, and how well, do they work? Visit anatomy of snake to learn about snake body parts & their function. At rest they are like two inverted sacs either side of the midline and lie ventral to two other small invaginations in the tail which form the anal glands. Gravity strongly influences hemodynamics, and the impact on structure and function of the cardiovascular system, including pulmonary circulation, is.
Snake repellents — how, and how well, do they work? These are essentially the equivalent of two small penises. Combat bouts impose strong selection for large body size in males of some. Snakes have a small opening just behind the tongue called the glottis, which opens into the trachea, or windpipe. The vertebral column has more vertebrae than any other living animal—up to 600. [1] [2] [3] hemipenes are usually held inverted within the body, and are everted for reproduction via erectile tissue, much like that in the human penis. Each hemipenis has a retractor muscle that extends from the tail vertebrae to the tip and sides of the hemipene and.
Male Snake Anatomy
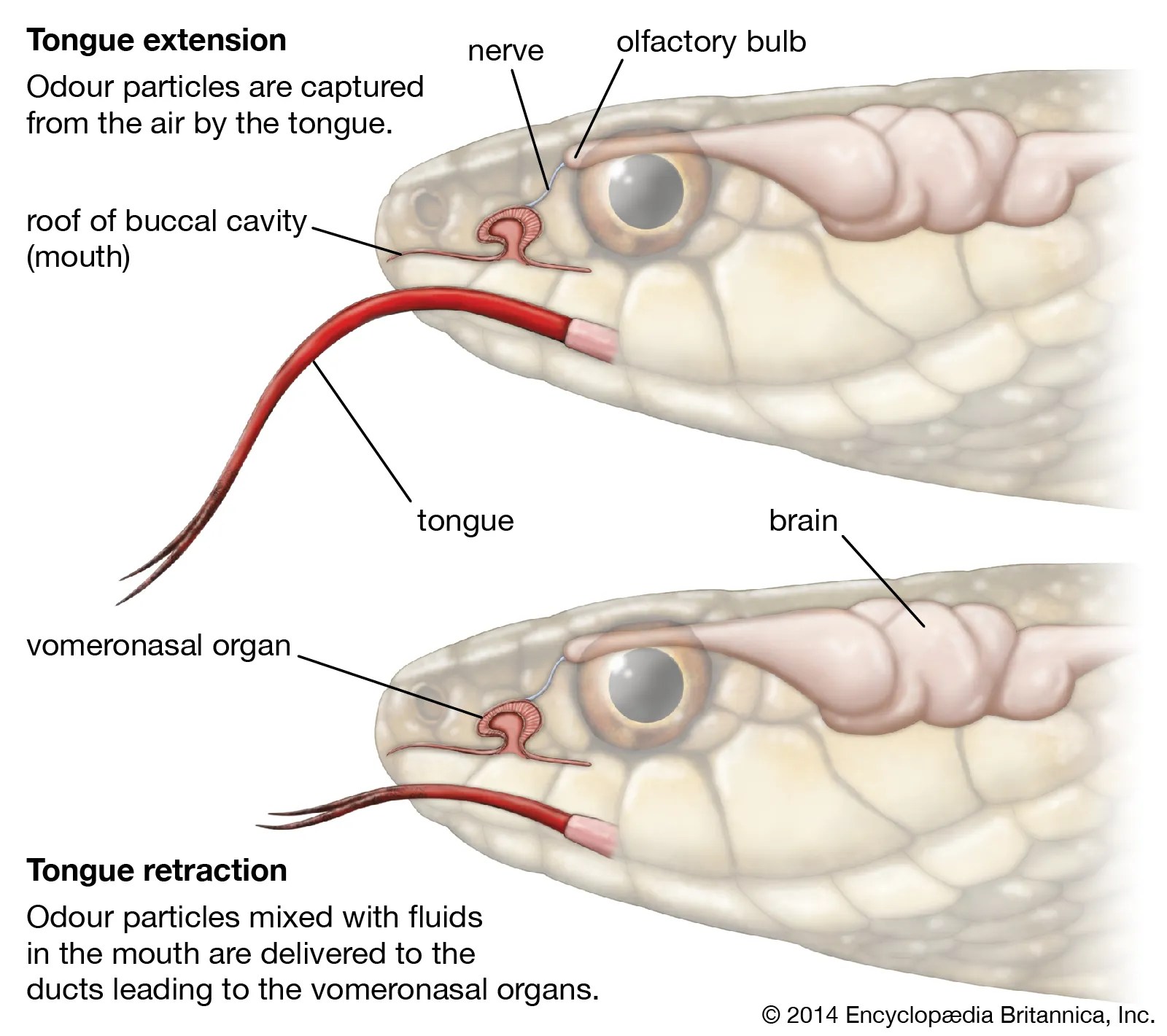
A sophisticated vomeronasal system not only allows male snakes to locate reproductive females by following scent trails, but also facilitates pheromonally mediated mate choice by males. Gravity strongly influences hemodynamics, and the impact on structure and function of the cardiovascular system, including pulmonary circulation, is. At rest they are like two inverted sacs either side.
Muscular System Rattlesnakes
Both male and female snakes have a cloaca for waste purposes, but a female’s is also used for reproduction purposes. The posterior part of the kidneys of most male snakes is sexually dimorphic. Visit anatomy of snake to learn about snake body parts & their function. At rest they are like two inverted sacs either.
All about snakes Wildlife
The penis of a crocodile or turtle is protruded through the cloacal opening wholly by means of a filling of blood space (sinuses) in the penis; Snakes have a long narrow body that can be divided into four quadrants. Reproductive anatomy & physiology in reptiles: Visit anatomy of snake to learn about snake body parts.
Anatomy Snake
A portion of the distal tubules, called the sexual segment, shows a seasonal enlargement and cellular changes. Gravity strongly influences hemodynamics, and the impact on structure and function of the cardiovascular system, including pulmonary circulation, is. Check out the internal & external snake anatomy diagram. The posterior part of the kidneys of most male snakes.
Male Snake Anatomy
They come in a variety of shapes, depending on species, with ornamentation such as. Kidneys, the cloaca, and for male snakes, the hemipenes are located in quadrant four. Instead, the kidneys filter the blood and drop urinary waste through the ureters and directly into the cloaca. The vertebral column has more vertebrae than any other.
Male Snake Anatomy
The hemipenes of lizards and snakes are elongated tubular structures lying in the tail. The penis of a crocodile or turtle is protruded through the cloacal opening wholly by means of a filling of blood space (sinuses) in the penis; Snakes have a small opening just behind the tongue called the glottis, which opens into.
Structure Of A Snake
The gallbladder stores bile made by the liver. A phospholipid secretion is produced here and is. Visit anatomy of snake to learn about snake body parts & their function. Each part has a specific function, or job. University of sydney researcher christopher friesen says having two hemipenes may benefit males during mating. Snake repellents —.
Anatomy of a Snake by MeganMosier on DeviantArt
Major structures of the first quadrant consist of the head, esophagus, heart, and trachea. The posterior part of the kidneys of most male snakes is sexually dimorphic. Visit anatomy of snake to learn about snake body parts & their function. Let’s explore the snake anatomy — their faces, skeleton, body, and more! Snakes have a.
Male Snake Anatomy
The hemipenes of lizards and snakes are elongated tubular structures lying in the tail. The penis of a crocodile or turtle is protruded through the cloacal opening wholly by means of a filling of blood space (sinuses) in the penis; Each hemipenis has a retractor muscle that extends from the tail vertebrae to the tip.
Snake anatomy Diagram Quizlet
Male snakes and their hemipenes • snake hemipenes revealed • discover the unique anatomy of male snakes and learn about their paired. Let’s explore the snake anatomy — their faces, skeleton, body, and more! Snakes and lizards have not just one, but two penises, called hemipenes. At rest they are like two inverted sacs either.
Male Snake Anatomy Kidneys, the cloaca, and for male snakes, the hemipenes are located in quadrant four. Both male and female snakes have a cloaca for waste purposes, but a female’s is also used for reproduction purposes. Its paired openings are just in front of the snake’s choana, the open slitlike structure on. The path from the mouth to the stomach. These are essentially the equivalent of two small penises.
[1] [2] [3] Hemipenes Are Usually Held Inverted Within The Body, And Are Everted For Reproduction Via Erectile Tissue, Much Like That In The Human Penis.
Snakes have a long narrow body that can be divided into four quadrants. A crisp, higher resolution of this graphic is contained on australia's reptiles cdrom. The posterior part of the kidneys of most male snakes is sexually dimorphic. Hemipenes) is one of a pair of intromittent organs of male squamates (snakes and lizards).
University Of Sydney Researcher Christopher Friesen Says Having Two Hemipenes May Benefit Males During Mating.
They come in a variety of shapes, depending on species, with ornamentation such as. What makes a snake a snake? Snake anatomy, physiology, and taxonomy. The complex and successful evolutionary history of snakes produced variation in the position and structure of internal organs.
Snakes Don’t Have A Bladder, So They Don’t Store Urine.
A phospholipid secretion is produced here and is. Both male and female snakes have a cloaca for waste purposes, but a female’s is also used for reproduction purposes. The penis is a male reproductive organ. Male snakes and their hemipenes • snake hemipenes revealed • discover the unique anatomy of male snakes and learn about their paired.
Major Structures Of The First Quadrant Consist Of The Head, Esophagus, Heart, And Trachea.
A snake's body is made up of many parts. Unlike what mammals have, the reptile glottis is always closed, forming a vertical slit, unless the snake takes a breath. Snakes have an elongated body and tail, and no limbs. Snakes have two penises, each of which is called a hemipenis.