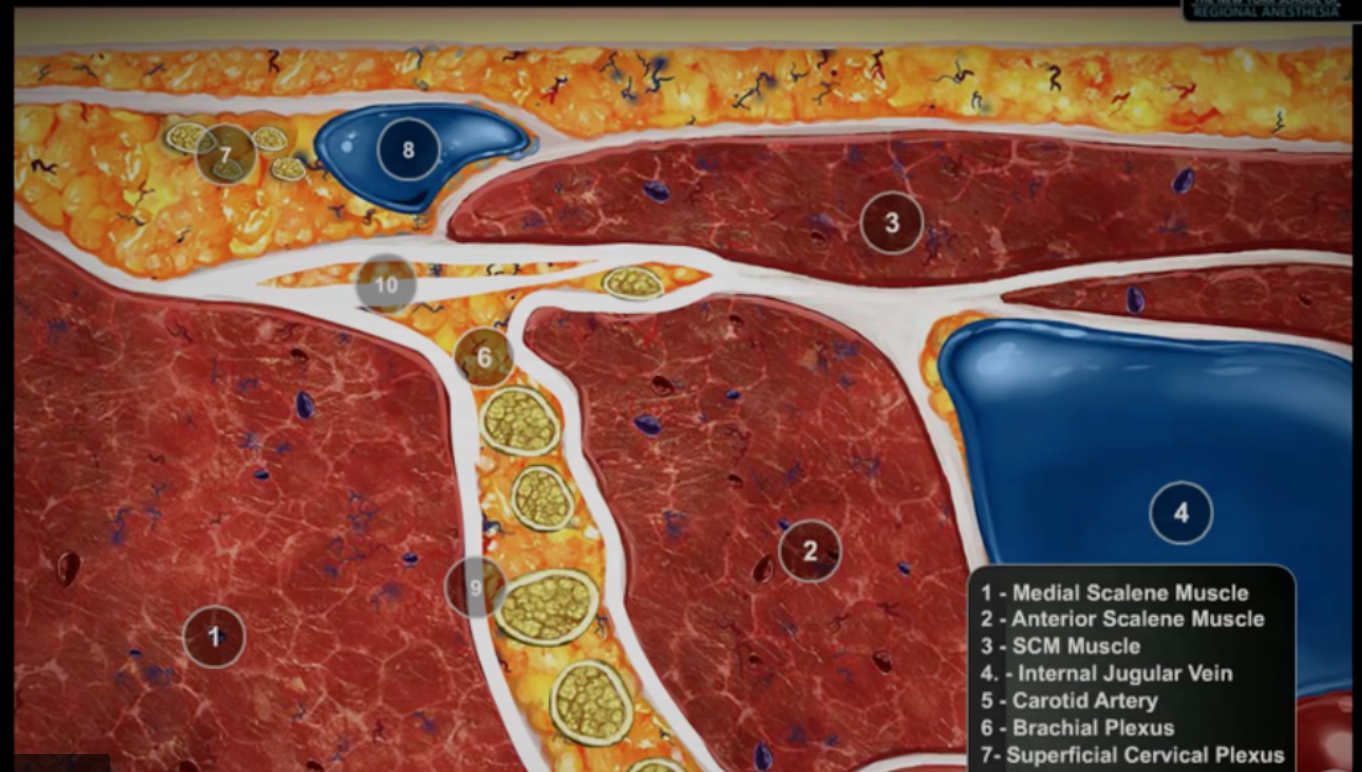
Interscalene Block Anatomy - A practical approach to peripheral nerve blocks and perineural catheters.
Interscalene Block Anatomy - Web the roots and trunks pass through the interscalene groove, a palpable surface anatomic landmark between the anterior and middle scalene muscles. A practical approach to peripheral nerve blocks and perineural catheters. The roots originate from the ventral rami of cervical (c) spinal. The aim of this procedure is to block the brachial plexus trunks in the interscalene groove between the anterior and middle scalene muscles. The brachial plexus is formed by the ventral rami of c5 to t1 nerve roots.
The plexus (bp) is seen between the middle scalene muscle. The roots of the brachial plexus are found in the interscalene groove between the anterior and middle scalene muscles at the level of the cricoid cartilage (c6) in the neck. Web the interscalene brachial plexus block is a common regional anesthesia technique for anesthesia and analgesia of the shoulder and upper arm surgery, as it provides. Web the interscalene block (isb) anesthetizes the brachial plexus at the level of the nerve roots, and is used for surgery of the upper arm, shoulder, and neck. The brachial plexus innervates the shoulder and upper limb (figure 1). Web the roots and trunks pass through the interscalene groove, a palpable surface anatomic landmark between the anterior and middle scalene muscles. The aim of this procedure is to block the brachial plexus trunks in the interscalene groove between the anterior and middle scalene muscles.
UltrasoundGuided Interscalene Brachial Plexus Nerve Block Core EM
The plexus (bp) is seen between the middle scalene muscle. The brachial plexus is commonly blocked at interscalene level for surgeries involving the clavicle, shoulder and upper arm. The aim of this procedure is to block the brachial plexus trunks in the interscalene groove between the anterior and middle scalene muscles. Web the interscalene block.
UltrasoundGuided Interscalene Block WFSA Resources
The plexus is formed by the ventral rami of the fifth to eighth cervical nerves and the greater part of the ventral ramus of the first thoracic nerve ( figure 1 ). A practical approach to peripheral nerve blocks and perineural catheters. Web interscalene block is the most proximal approach to the brachial plexus and.
UltrasoundGuided Interscalene Brachial Plexus Nerve Block Core EM
Web interscalene block is the most proximal approach to the brachial plexus and is the most suitable block for proximal procedures on the arm or shoulder. Web the roots and trunks pass through the interscalene groove, a palpable surface anatomic landmark between the anterior and middle scalene muscles. The plexus is formed by the ventral.
Interscalene Block // Ultrasound Anatomy Review YouTube
The roots of the brachial plexus are found in the interscalene groove between the anterior and middle scalene muscles at the level of the cricoid cartilage (c6) in the neck. Web the interscalene block (isb) anesthetizes the brachial plexus at the level of the nerve roots, and is used for surgery of the upper arm,.
UltrasoundGuided Interscalene Brachial Plexus Block Video NYSORA The
The brachial plexus is commonly blocked at interscalene level for surgeries involving the clavicle, shoulder and upper arm. The brachial plexus is formed by the ventral rami of c5 to t1 nerve roots. The brachial plexus innervates the shoulder and upper limb (figure 1). The plexus is formed by the ventral rami of the fifth.
UltrasoundGuided Interscalene Brachial Plexus Nerve Block Core EM
A practical approach to peripheral nerve blocks and perineural catheters. The roots of the brachial plexus are found in the interscalene groove between the anterior and middle scalene muscles at the level of the cricoid cartilage (c6) in the neck. The brachial plexus is formed by the ventral rami of c5 to t1 nerve roots..
UltrasoundGuided Interscalene Block WFSA Resources
The roots of the brachial plexus are found in the interscalene groove between the anterior and middle scalene muscles at the level of the cricoid cartilage (c6) in the neck. Hadzic's peripheral nerve blocks and anatomy for ultrasound. The plexus is formed by the ventral rami of the fifth to eighth cervical nerves and the.
Interscalene — Highland EM Ultrasound Fueled pain management
Web interscalene block is the most proximal approach to the brachial plexus and is the most suitable block for proximal procedures on the arm or shoulder. The plexus is formed by the ventral rami of the fifth to eighth cervical nerves and the greater part of the ventral ramus of the first thoracic nerve (.
USGuided Interscalene Brachial Plexus Block Regional anesthesia
The brachial plexus innervates the shoulder and upper limb (figure 1). Hadzic's peripheral nerve blocks and anatomy for ultrasound. Web interscalene block is the most proximal approach to the brachial plexus and is the most suitable block for proximal procedures on the arm or shoulder. Web the roots and trunks pass through the interscalene groove,.
Interscalene « VAULT
The roots originate from the ventral rami of cervical (c) spinal. A practical approach to peripheral nerve blocks and perineural catheters. The brachial plexus innervates the shoulder and upper limb (figure 1). Web the interscalene block (isb) anesthetizes the brachial plexus at the level of the nerve roots, and is used for surgery of the.
Interscalene Block Anatomy The plexus (bp) is seen between the middle scalene muscle. Web the interscalene brachial plexus block is a common regional anesthesia technique for anesthesia and analgesia of the shoulder and upper arm surgery, as it provides. A practical approach to peripheral nerve blocks and perineural catheters. The plexus is formed by the ventral rami of the fifth to eighth cervical nerves and the greater part of the ventral ramus of the first thoracic nerve ( figure 1 ). Web interscalene block is the most proximal approach to the brachial plexus and is the most suitable block for proximal procedures on the arm or shoulder.
The Brachial Plexus Innervates The Shoulder And Upper Limb (Figure 1).
The aim of this procedure is to block the brachial plexus trunks in the interscalene groove between the anterior and middle scalene muscles. The roots of the brachial plexus are found in the interscalene groove between the anterior and middle scalene muscles at the level of the cricoid cartilage (c6) in the neck. Hadzic's peripheral nerve blocks and anatomy for ultrasound. Web interscalene block is well suited for surgical procedures involving the shoulder, including the lateral two thirds of the clavicle, proximal humerus, and shoulder joint.
A Practical Approach To Peripheral Nerve Blocks And Perineural Catheters.
Web the interscalene brachial plexus block is a common regional anesthesia technique for anesthesia and analgesia of the shoulder and upper arm surgery, as it provides. The plexus (bp) is seen between the middle scalene muscle. The brachial plexus is commonly blocked at interscalene level for surgeries involving the clavicle, shoulder and upper arm. Web the interscalene block (isb) anesthetizes the brachial plexus at the level of the nerve roots, and is used for surgery of the upper arm, shoulder, and neck.
The Plexus Is Formed By The Ventral Rami Of The Fifth To Eighth Cervical Nerves And The Greater Part Of The Ventral Ramus Of The First Thoracic Nerve ( Figure 1 ).
Web interscalene block is the most proximal approach to the brachial plexus and is the most suitable block for proximal procedures on the arm or shoulder. The brachial plexus is formed by the ventral rami of c5 to t1 nerve roots. The roots originate from the ventral rami of cervical (c) spinal. Web the roots and trunks pass through the interscalene groove, a palpable surface anatomic landmark between the anterior and middle scalene muscles.