Identify The Enol Form Of Each Keto Tautomer - The relative stability of these two.
Identify The Enol Form Of Each Keto Tautomer - If, however, protonation takes place on the. And so you could imagine,. Web which of the following have an enol form?i. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert. A b c d this problem has been solved!
1) protonation of the carbonyl. If, however, protonation takes place on the. A b c d this problem has been solved! Web which of the following have an enol form?i. This problem has been solved! You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn. They're isomers of each other so we call them tautomers and they're in equilibrium with each other.
Keto Enol Tautomerization Reaction and Mechanism in Acid and Base
Web the keto form and the enol form, and these are different molecules. The preferred enol tautomer form can be. Web which of the following have an enol form?i. At the same time, we need to remove the hydroxyl group (oh) from the carbon and replace it with a hydrogen atom (h). Web if protonation.
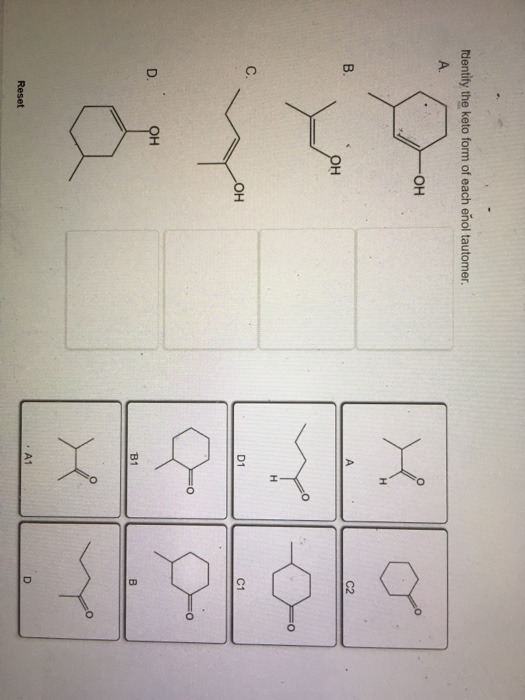
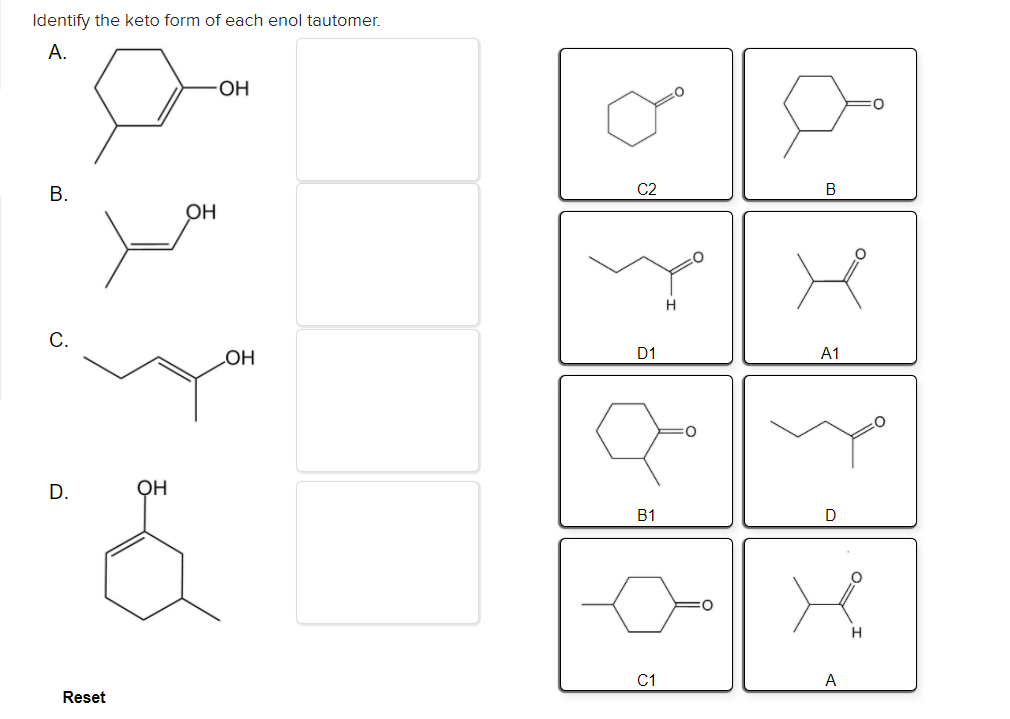
Solved Identify the keto form of each enol tautomer. А. ОН
Web alkehydes and symmetrical ketones typically only have one possible enol tautomer while asymmetrical ketones have two or more. Identify the enol form of each keto tautomer. 1) protonation of the carbonyl. Acids and bases both bring about the. The relative stability of these two. The preferred enol tautomer form can be. If, however, protonation.
[Solved] What is the predominant enol tautomer of 9to5Science
At the same time, we need to remove the hydroxyl group (oh) from the carbon and replace it with a hydrogen atom (h). Web identify the keto form of the enol tautomer shown below: Web which of the following have an enol form?i. Web if protonation of the enolate ion takes place on the α.
Keto Enol Tautomerism What Is It and Why Is It Important?
It can spontaneously through equilibrium get to the actual enol form. Web identify the keto form of the enol tautomer shown below: Acids and bases both bring about the. The preferred enol tautomer form can be. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn. You'll get a detailed solution.
Keto Enol Tautomerism A Summary of Key Points — Master Organic Chemistry
Web the keto form and the enol form, and these are different molecules. It can spontaneously through equilibrium get to the actual enol form. The relative stability of these two. Web identify the keto form of the enol tautomer shown below: 1) protonation of the carbonyl. Web if protonation of the enolate ion takes place.
Ketoenol tautomerism reaction Royalty Free Vector Image
The relative stability of these two. Identify the enol form of each keto tautomer. 1) protonation of the carbonyl. At the same time, we need to remove the hydroxyl group (oh) from the carbon and replace it with a hydrogen atom (h). They're isomers of each other so we call them tautomers and they're in.
Keto Enol Tautomerism A Summary of Key Points — Master Organic Chemistry
Tautomers are readily interconverted constitutional isomers, usually distinguished by a different location for an atom or a group. Web alkehydes and symmetrical ketones typically only have one possible enol tautomer while asymmetrical ketones have two or more. They're isomers of each other so we call them tautomers and they're in equilibrium with each other. 1).
Solved dentify the keto form of each enol tautomer он C2 C.
Web alkehydes and symmetrical ketones typically only have one possible enol tautomer while asymmetrical ketones have two or more. The preferred enol tautomer form can be. The relative stability of these two. A b c d this problem has been solved! And so you could imagine,. It can spontaneously through equilibrium get to the actual.
Solved Identify the enol form of each keto tautomer.
It can spontaneously through equilibrium get to the actual enol form. This problem has been solved! Tautomers are readily interconverted constitutional isomers, usually distinguished by a different location for an atom or a group. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert. A b c d this problem has been solved! At the.
KetoEnol Tautomerism Key Points Master Organic Chemistry
And so you could imagine,. The preferred enol tautomer form can be. This problem has been solved! A b c d this problem has been solved! It can spontaneously through equilibrium get to the actual enol form. Web the keto form and the enol form, and these are different molecules. You'll get a detailed solution.
Identify The Enol Form Of Each Keto Tautomer This problem has been solved! And so you could imagine,. Web identify the keto form of the enol tautomer shown below: Web in a solution, you won't see much of the enol form, but these can occur. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert.
Web Identify The Keto Form Of The Enol Tautomer Shown Below:
And so you could imagine,. Web alkehydes and symmetrical ketones typically only have one possible enol tautomer while asymmetrical ketones have two or more. If, however, protonation takes place on the. A b c d this problem has been solved!
1) Protonation Of The Carbonyl.
Web which of the following have an enol form?i. Web if protonation of the enolate ion takes place on the α carbon, the keto tautomer is regenerated and no net change occurs. Web the keto form and the enol form, and these are different molecules. Web in a solution, you won't see much of the enol form, but these can occur.
It Can Spontaneously Through Equilibrium Get To The Actual Enol Form.
You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert. Acids and bases both bring about the. The preferred enol tautomer form can be. At the same time, we need to remove the hydroxyl group (oh) from the carbon and replace it with a hydrogen atom (h).
Identify The Enol Form Of Each Keto Tautomer.
They're isomers of each other so we call them tautomers and they're in equilibrium with each other. This problem has been solved! You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn. Tautomers are readily interconverted constitutional isomers, usually distinguished by a different location for an atom or a group.


![[Solved] What is the predominant enol tautomer of 9to5Science](https://i2.wp.com/i.stack.imgur.com/FsOH2.jpg)