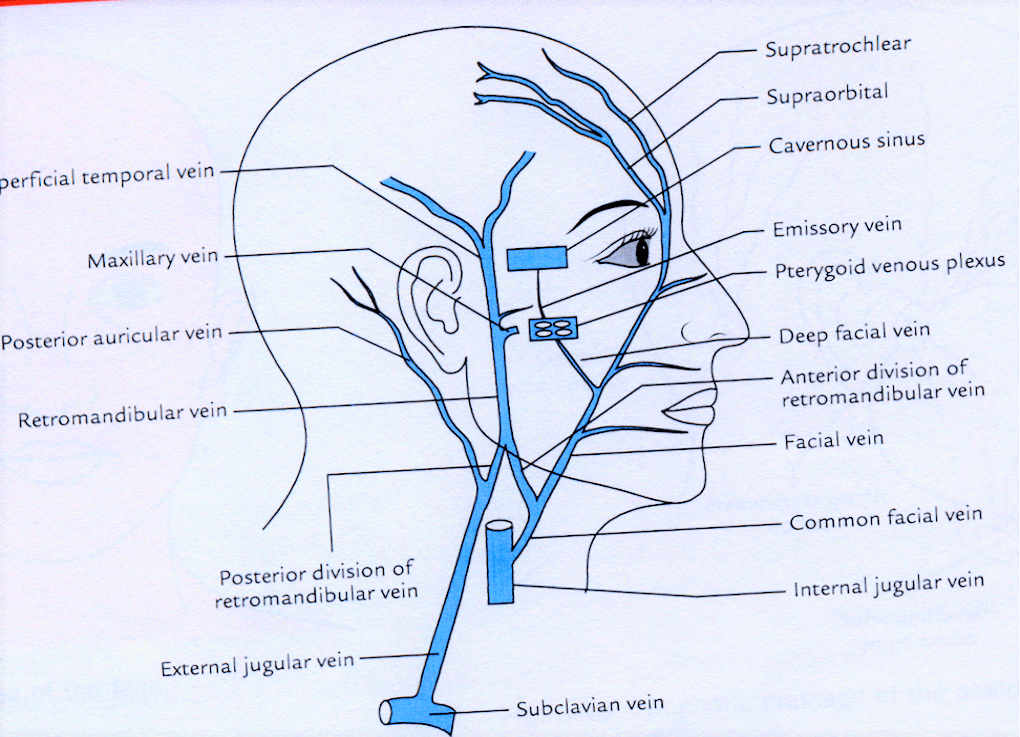
Face Veins Anatomy - Venous drainage of the scalp and face:
Face Veins Anatomy - The veins of the head and neck collect deoxygenated blood and return it to the heart. At the level of the lower margin of the orbit, the angular vein becomes the facial vein 1. Vena facialis) is a venous blood vessel that is a continuation of the angular vein. Describe the formation, course, termination and connections of facial vein. The retromandibular vein, also known as the posterior facial vein, is a deep vein of the face that is formed by the merger of the superficial temporal vein with the maxillary vein.
This illustration was published in. Upper face, middle face, and lower face. The common facial vein is formed by the union of the anterior division of the retromandibular vein with the facial vein. The facial vein, also referred to as the anterior facial vein, is a paired vessel and the main vein of the face. The pharynx is the medical term for the throat. It lies behind the facial artery and follows a less tortuous course. Venous drainage of the scalp and face:
FACE_Anatomy_muscle_veins_Detailed_EDUCATIONAL_SCIENCE_poster1 Etsy
Anatomically, the venous drainage can be divided into three parts: The facial vein, also referred to as the anterior facial vein, is a paired vessel and the main vein of the face. The main venous drainage of the face is completed by the facial, buccal, mental, and infraorbital veins. The veins of the head and.
Face Venous and Lymphatic Drainage Anatomy QA
The facial vein is a direct continuation of the angular vein that occurs at the approximate level of the inner canthus of the eye. Major veins of the face and scalp include the facial vein, which drains into the internal jugular vein, and the posterior auricular, which drains into the external jugular vein, among others.
Major Arteries and Veins of the Face. Vector Medical Illustration Stock
It starts as a continuation of the angular vein (read more!) at the level of the inferior margin of the bony orbit. Vena facialis) is a venous blood vessel that is a continuation of the angular vein. The common facial vein is formed by a joining together of veins that drain the face, the infratemporal.
Vessels and veins by KevinCease on DeviantArt in 2020 Facial anatomy
Drained by veins synonymous with the arteries of the face and scalp. Anatomically, the venous drainage can be divided into three parts: The facial veins stem from the angular veins on each side of the root of the nose. The facial vein, also referred to as the anterior facial vein, is a paired vessel and.
Superficial arteries and veins of the face and scalp Kenhub
The facial vein is a direct continuation of the angular vein that occurs at the approximate level of the inner canthus of the eye. The facial vein usually unites with the anterior branch of the retromandibular vein to form the common facial vein, which crosses the external carotid artery and enters the internal jugular vein.
face_1_all_by_kevinceased6rgbdj.jpg (1024×1304) Facial anatomy, Face
Anatomically, the venous drainage can be divided into three parts: Venous drainage of the brain and meninges: Discover the origin, course, and drainage of the common facial vein, including its union with the facial and retromandibular veins. The internal jugular vein continues down the neck, behind the common carotid artery and lateral to it. The.
Face Venous and Lymphatic Drainage Anatomy QA
The facial vein is a direct continuation of the angular vein that occurs at the approximate level of the inner canthus of the eye. Major veins of the face and scalp include the facial vein, which drains into the internal jugular vein, and the posterior auricular, which drains into the external jugular vein, among others.
Labeling Deep Facial Vein Drainage
The facial vein starts from the medial aspect of the eye as the angular vein reaches the infraorbital margin. Major veins of the face and scalp include the facial vein, which drains into the internal jugular vein, and the posterior auricular, which drains into the external jugular vein, among others (see the overview image above)..
Face Muscles, Facial artery and Vein, Nerve supply Anatomy QA
The facial vein, also referred to as the anterior facial vein, is a paired vessel and the main vein of the face. The facial vein (anterior facial vein) commences at the side of the root of the nose, and is a direct continuation of the angular vein. It is formed by the confluence of two.
Facial Anatomy Veins And Arteries
The pharynx is the medical term for the throat. The facial veins stem from the angular veins on each side of the root of the nose. The veins of the head and neck collect deoxygenated blood and return it to the heart. It is usually called the facial vein once below the adjoining level of.
Face Veins Anatomy The facial vein (or anterior facial vein) is a relatively large vein in the human face. The facial vein, also referred to as the anterior facial vein, is a paired vessel and the main vein of the face. The pharynx is also what helps you talk, as muscles in the throat vibrate to help make sound. Vena facialis) is a venous blood vessel that is a continuation of the angular vein. The facial vein, sometimes also called the anterior facial vein, is an extracranial vein of the head and the main vessel collecting deoxygenated blood from the structures of the face.
The Pharynx Is The Medical Term For The Throat.
The common facial vein is formed by the union of the anterior division of the retromandibular vein with the facial vein. They drain into the internal jugular or the pterygoid plexus. The anatomy of the face can divide into three main regions: The facial vein usually unites with the anterior branch of the retromandibular vein to form the common facial vein, which crosses the external carotid artery and enters the internal jugular vein at a variable point below the hyoid bone.
It Runs Within The Substance Of The Parotid Gland, Descending Posterior To The Ramus Of The Mandible.
The veins of the head and neck collect deoxygenated blood and return it to the heart. The retromandibular vein, also known as the posterior facial vein, is a deep vein of the face that is formed by the merger of the superficial temporal vein with the maxillary vein. The venous drainage of the scalp is rich and is provided by the occipital, posterior auricular, and superficial temporal veins. Describe the formation, course, termination and connections of facial vein.
Discover The Origin, Course, And Drainage Of The Common Facial Vein, Including Its Union With The Facial And Retromandibular Veins.
The facial vein (along with the facial artery) pierces the neck's deep investing fascia just below the mandible's border, where it unites with the anterior branch of the retromandibular vein to form the common facial. The facial vein (or anterior facial vein) is a relatively large vein in the human face. The function of the pharynx is to take in air from the nasal passages as well as food and drink from the mouth. The anterior vein runs a path down and backward through the face.
It Commences At The Side Of The Root Of The Nose And Is A Direct Continuation Of The Angular Vein Where It Also Receives A Small Nasal Branch.
The facial vein is a direct continuation of the angular vein that occurs at the approximate level of the inner canthus of the eye. The facial vein, also referred to as the anterior vein of the face, begins from the angular vein at the bottom of the nose. It is formed by the confluence of two roots, namely the superficial root being the angular vein and the deep root being the profound vein of the face. At the level of the lower margin of the orbit, the angular vein becomes the facial vein 1.





:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/2367/g9iS09d9qkjtMbCGR7Y3Q_superficial-arteries-of-the-head-lateral_english.jpg)