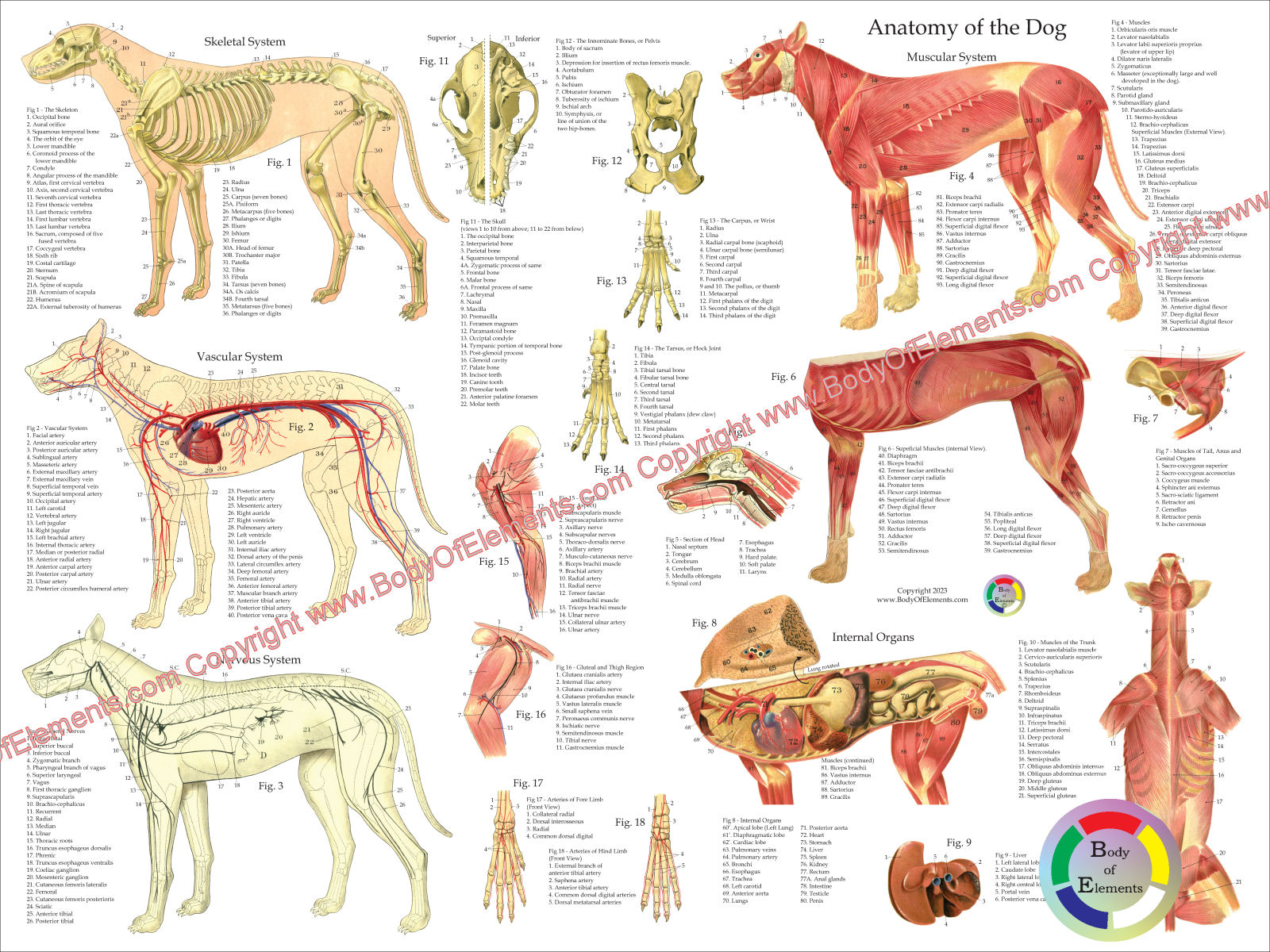
External Anatomy Of Dog - The external anatomy of a dog.
External Anatomy Of Dog - Upper arm bone radius and ulna: This veterinary anatomy module contains 608 illustrations on the canine myology. The smallest breeds include the toy and miniature varieties, such as the toy poodle, papillon, chihuahua, and shih tzu. The inner ear is a complex structure that includes the cochlea (the organ of hearing) and the vestibular system (the organ of balance). Here are presented scientific illustrations of the canine muscles and skeleton from different anatomical standard views (lateral, medial, cranial, caudal, dorsal, ventral / palmar.).
By exploring the different body parts and their functions, we can appreciate the complexity and beauty of a dog’s design. It also includes 2 muscles, the oval window, and the eustachian tube (a small tube that connects the middle ear with the back of the nose, allowing air to enter the middle ear). We discuss the internal and external anatomy of dogs so that you can see that, despite individual differences, there is a reason they are all considered part of the same species. Again, you will find the details anatomy of the nasal conchae, meatus, paranasal sinuses, and glands from the dog’s nasal cavity. The detailing of these structures changes based on dog breed due to the huge variation of size in dog breeds. Like the back legs, they have complex anatomy. Upper arm bone radius and ulna:
External Anatomy Of A Dog Stock Vector Illustration 172987946
A dog’s front legs bear about 2/3 of a dog’s total body weight. Having a good piece of knowledge on the dog’s external anatomy helps you understand the principles of your dog’s care and management. The head of a dog is one of its most distinguishing features. From the external part of a dog’s nose,.
Canine External Anatomy Anatomy and Physiology Veterinary Medical
The inner ear is a complex structure that includes the cochlea (the organ of hearing) and the vestibular system (the organ of balance). By exploring the different body parts and their functions, we can appreciate the complexity and beauty of a dog’s design. Directional terms include cranial, caudal, rostral, dorsal, palmar, plantar, medial, and lateral..
Dog External Anatomy
These include the head, ears, eyes, nose, mouth, neck, tail, legs, and paws. As a dog enthusiast it is important to know the parts of a dog. The reason for the glowing appearance lies in a structure that canines and. The loin is the back between the end of the rib cage and the beginning.
Dog External Anatomy. Puppy Parts on English Stock Vector
As a dog enthusiast it is important to know the parts of a dog. This is 44 times the number of receptors in a human nose. It includes the skull, jaw, and teeth. The dog nose anatomy comprises external features and the structures of the nasal cavity. These include the head, ears, eyes, nose, mouth,.
Dog Domestication Britannica
A dog’s front legs bear about 2/3 of a dog’s total body weight. External anatomy (topography) of a typical dog: Dewlap (throat, neck skin) 4. Upper arm bone radius and ulna: Dog anatomy details the various structures of canines (e.g. Now, i will discuss the different parts from the five different areas of the dog’s.
The Ultimate Dog Anatomy Guide 2022 — Sidekick by Finn
Feb 24, 2022 | last update: It includes the skull, jaw, and teeth. Directional terms from anatomic position in dogs are more directly compared with the directional terms in humans when the human is in a quadruped position or the dog is in an upright stance posture. The external parts of a dog. The female.
Understanding Your Dog's Body A Detailed Anatomy Overview sample
These dogs usually weigh only 5 to 10 pounds (2.3 to 4.5 kilograms), or even less. Having a good piece of knowledge on the dog’s external anatomy helps you understand the principles of your dog’s care and management. External anatomy (topography) of a typical dog: The reason for the glowing appearance lies in a structure.
Dog Anatomy The Y Guide
The loin is the back between the end of the rib cage and the beginning of the pelvic bone. Now, i will discuss the different parts from the five different areas of the dog’s body. Dewlap (throat, neck skin) 4. These dogs usually weigh only 5 to 10 pounds (2.3 to 4.5 kilograms), or even.
dogexternalanatomy ESL Buzz
The inner ear is a complex structure that includes the cochlea (the organ of hearing) and the vestibular system (the organ of balance). The anatomy of a dog includes its skeletal structure, reproductive system, the internal organs, and its external appearance. You may also be interested in: The outside appearance and the external body parts.
external_anatomy2 Pure Dog Talk
Feb 24, 2022 | last update: Directional terms from anatomic position in dogs are more directly compared with the directional terms in humans when the human is in a quadruped position or the dog is in an upright stance posture. It also includes 2 muscles, the oval window, and the eustachian tube (a small tube.
External Anatomy Of Dog Dog anatomy details the various structures of canines (e.g. We discuss the internal and external anatomy of dogs so that you can see that, despite individual differences, there is a reason they are all considered part of the same species. The loin is the back between the end of the rib cage and the beginning of the pelvic bone. A dog’s front legs bear about 2/3 of a dog’s total body weight. The uterus becomes the womb for her puppies during their gestation period.
It Also Includes 2 Muscles, The Oval Window, And The Eustachian Tube (A Small Tube That Connects The Middle Ear With The Back Of The Nose, Allowing Air To Enter The Middle Ear).
Upper arm bone radius and ulna: The belly or abdomen is the underside of the dog from the end of its rib cage to its tail. We discuss the internal and external anatomy of dogs so that you can see that, despite individual differences, there is a reason they are all considered part of the same species. Fully labeled illustrations and diagrams of the dog (skeleton, bones, muscles, joints, viscera, respiratory system, cardiovascular system).
You May Notice This Phenomenon If You Try To Photograph Your Dog At Night.
Having a good piece of knowledge on the dog’s external anatomy helps you understand the principles of your dog’s care and management. You may also be interested in: Dewlap (throat, neck skin) 4. The head of a dog is one of its most distinguishing features.
The Loin Is The Back Between The End Of The Rib Cage And The Beginning Of The Pelvic Bone.
A dog’s front legs bear about 2/3 of a dog’s total body weight. These dogs usually weigh only 5 to 10 pounds (2.3 to 4.5 kilograms), or even less. A pregnant female dog's anatomy includes two ovaries, which produce eggs, the cervix, fallopian tubes, and the uterus. The following paragraphs explain all these aspects in brief, along with diagrams, which will help you understand them better.
Directional Terms From Anatomic Position In Dogs Are More Directly Compared With The Directional Terms In Humans When The Human Is In A Quadruped Position Or The Dog Is In An Upright Stance Posture.
The reason for the glowing appearance lies in a structure that canines and. Gain a comprehensive understanding of your dog's health with our veterinary guide to cat anatomy complete with diagrams, images and simple explanations. Feb 24, 2022 | last update: The indentation in a dog’s forehead just above eye level & varies in depth by breed.