Equine Limb Anatomy - This limb carries 55 to 60 percent of the horse’s body weight, and a large proportion of the rider’s weight as well.
Equine Limb Anatomy - The limbs of the horse are structures made of many bones, joints, muscles, tendons and ligaments that support the weight of the horse’s body. The author uses a variety of diagnostic modalities to illustrate the normal anatomy of the equine distal limb. Explanations in the book describe how to avoid surgical infections, select and use instruments, and perfect fundamental surgical techniques including incisions, cautery, retractions, irrigation, surgical suction, wound closure, dressings, bandages, and casts. This is an online quiz called equine distal limb. You can use it as equine distal limb practice, completely free to play.
Read our guide to equine distal limb anatomy to find out more about the bones, tendons and ligaments in the horse’s legs. There are nine bones total and each plays a vital role in movement and stability. You can use it as equine distal limb practice, completely free to play. Explanations in the book describe how to avoid surgical infections, select and use instruments, and perfect fundamental surgical techniques including incisions, cautery, retractions, irrigation, surgical suction, wound closure, dressings, bandages, and casts. The objective of this report was to provide an anatomic description of the equine palmar lateral outpouching of the middle carpal joint by comparing its arthroscopic and magnetic resonance (mr. The limbs play a major role in the movement of the horse, with the legs performing the functions of absorbing impact, bearing weight and providing thrust. In this article, we’ll take a tour of equine foot/lower limb anatomy and physiology with parks as our guide.
Horse Distal Limb Anatomy
There are nine bones total and each plays a vital role in movement and stability. In this article, we’ll take a tour of equine foot/lower limb anatomy and physiology with parks as our guide. To do this, a good understanding of equine anatomy is essential. The objective of this report was to provide an anatomic.
Vitals & Anatomy Horse Side Vet Guide
There is no muscle below the knee and hock. The limbs of the horse are structures made of many bones, joints, muscles, tendons and ligaments that support the weight of the horse’s body. Quick reference images of equine vitals and anatomy. Physiological cross sectional area was then determined and maximum isometric force estimated. Explanations in.
Vitals & Anatomy Horse Side Vet Guide
The limbs of the horse are structures made of many bones, joints, muscles, tendons and ligaments that support the weight of the horse’s body. To do this, a good understanding of equine anatomy is essential. The equine hind limb is also referred to as the pelvic hind limb. When working with horses, it is important.
Equine Distal Limb Anatomical illustration Equines, Horse anatomy
Learn about the anatomy and imaging of the equine distal limb with interactive 3d models, videos and quizzes from the royal veterinary college. There is no muscle below the knee and hock. This is an online quiz called equine distal limb. The bulbous ends of the splint bones can be palpated easily on the live.
Equine Limb Anatomy Soft and Sound Hoof Care
Physiological cross sectional area was then determined and maximum isometric force estimated. There are nine bones total and each plays a vital role in movement and stability. The splint bone has been outlined, and the sesamoid bone has been circled. In the equine, the second carpal bone (c2) rests entirely on the medial splint bone.
Vitals & Anatomy Horse Side Vet Guide
Learn about the anatomy and imaging of the equine distal limb with interactive 3d models, videos and quizzes from the royal veterinary college. The suspensory ligament attaches between the splint bones, then branches out and attaches to the sesamoids. The limbs play a major role in the movement of the horse, with the legs performing.
Vitals & Anatomy Horse Side Vet Guide
The objective of this report was to provide an anatomic description of the equine palmar lateral outpouching of the middle carpal joint by comparing its arthroscopic and magnetic resonance (mr. To do this, a good understanding of equine anatomy is essential. Physiological cross sectional area was then determined and maximum isometric force estimated. The equine.
Equine Limb Specializations
Equest's mission is to enhance the quality of life for children and adults with diverse needs by partnering with horses to bring hope and healing through equine assisted. Quick reference images of equine vitals and anatomy. The forelimb (also known as the thoracic limb) in the horse is adapted for extension and ground covering. The.
Vitals & Anatomy Horse Side Vet Guide
There are nine bones total and each plays a vital role in movement and stability. The legs of a horse are made up of a system of various apparatuses composed of muscles, ligaments, tendons, and connective tissue that work together to support the horse as it stands and to diminish compression during movement, thereby protecting.
Vitals & Anatomy Horse Side Vet Guide
Quick reference images of equine vitals and anatomy. The splint bone has been outlined, and the sesamoid bone has been circled. The equine hind limb is also referred to as the pelvic hind limb. The suspensory apparatus, which carries much of the weight, prevents overextension of the joint and absorbs shock, and the stay apparatus.
Equine Limb Anatomy The equine hind limb is also referred to as the pelvic hind limb. Colorized diagram of the tendons and ligaments of the equine distal limb assembled to view the various layers. The splint bone has been outlined, and the sesamoid bone has been circled. Specifically, we recorded muscle mass, fascicle length, pennation angle, tendon mass and tendon rest length. Equest's mission is to enhance the quality of life for children and adults with diverse needs by partnering with horses to bring hope and healing through equine assisted.
The Limbs Play A Major Role In The Movement Of The Horse, With The Legs Performing The Functions Of Absorbing Impact, Bearing Weight And Providing Thrust.
In this article, we’ll take a tour of equine foot/lower limb anatomy and physiology with parks as our guide. I find this a welcome addition to an atlas of anatomy. There is no muscle below the knee and hock. This limb carries 55 to 60 percent of the horse’s body weight, and a large proportion of the rider’s weight as well.
The Legs Of A Horse Are Made Up Of A System Of Various Apparatuses Composed Of Muscles, Ligaments, Tendons, And Connective Tissue That Work Together To Support The Horse As It Stands And To Diminish Compression During Movement, Thereby Protecting The Horse From Injuries To.
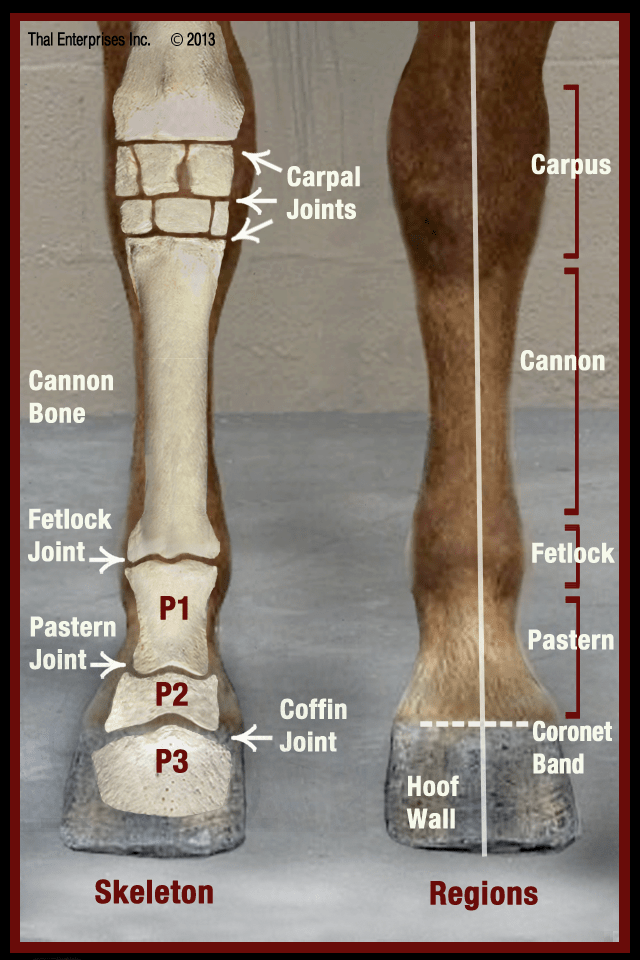
Be able to visualize the skeletal anatomy of the lower leg and hoof of the horse. Colorized diagram of the tendons and ligaments of the equine distal limb assembled to view the various layers. The suspensory apparatus, which carries much of the weight, prevents overextension of the joint and absorbs shock, and the stay apparatus , which locks major joints in. In the equine, the second carpal bone (c2) rests entirely on the medial splint bone (mc2) but the fourth carpal bone (c4) rests on both the cannon bone (mc3) and the lateral splint bone (mc4).
Read Our Guide To Equine Distal Limb Anatomy To Find Out More About The Bones, Tendons And Ligaments In The Horse’s Legs.
Home 3d radiographic projection select a body part and angle on the left, then select the type of image from the top menu. Equest's mission is to enhance the quality of life for children and adults with diverse needs by partnering with horses to bring hope and healing through equine assisted. There are nine bones total and each plays a vital role in movement and stability. The suspensory ligament attaches between the splint bones, then branches out and attaches to the sesamoids.
Learn About The Anatomy And Imaging Of The Equine Distal Limb With Interactive 3D Models, Videos And Quizzes From The Royal Veterinary College.
This is an online quiz called equine distal limb. The splint bone has been outlined, and the sesamoid bone has been circled. The distal limb is everything below the knee and the hock. The author uses a variety of diagnostic modalities to illustrate the normal anatomy of the equine distal limb.