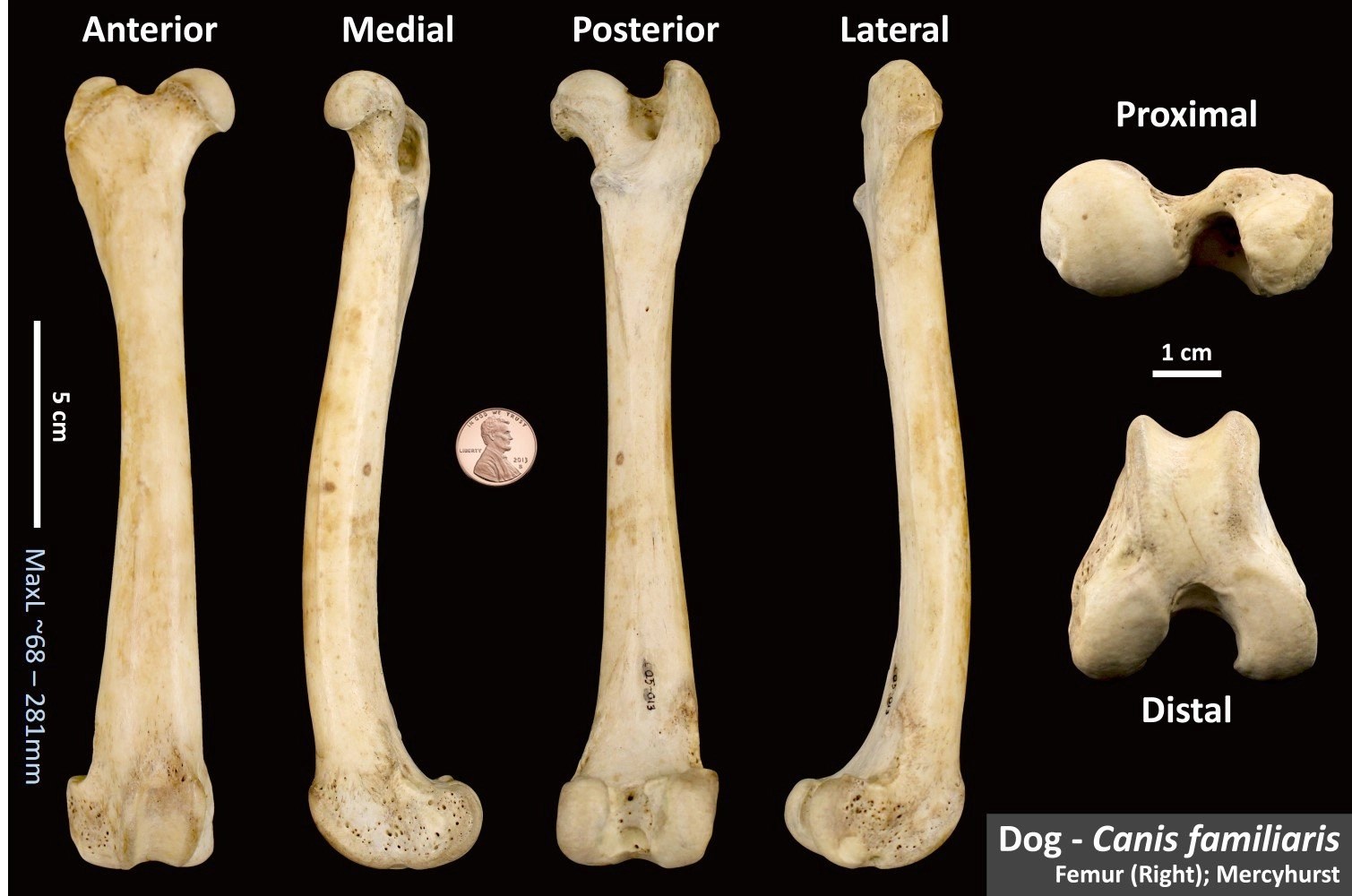
Dog Femur Anatomy - The distal portion of the dog femur is quadrangular and posses condyles and trochlea.
Dog Femur Anatomy - 4 development and growth of. The detailing of these structures changes based on dog breed due to the huge variation of size in dog breeds. 1 introduction to the femur: 2 structure and function of the femur: Fully labeled illustrations and diagrams of the dog (skeleton, bones, muscles, joints, viscera, respiratory system, cardiovascular system).
Positional and directional terms, general terminology and anatomical orientation are. The femur is a long (clyndircal) bone in the dog’s skeleton so that you will find all the typical osteological features. The detailing of these structures changes based on dog breed due to the huge variation of size in dog breeds. 4 development and growth of. Dog anatomy details the various structures of canines (e.g. Fully labeled illustrations and diagrams of the dog (skeleton, bones, muscles, joints, viscera, respiratory system, cardiovascular system). Muscle, organ and skeletal anatomy).
Canine Femur Anatomy
The largest bone in a dog’s body. Anatomy atlas of the canine general anatomy: You will find a nearly hemispherical head, neck, two processes, or trochanters at the proximal part of the dog femur. The distinction of the shape of the male and female pelvic inlet and outlet in humans is not made in dogs..
dog femur bone anatomy
4 development and growth of. 1 introduction to the femur: The largest bone in a dog’s body. Positional and directional terms, general terminology and anatomical orientation are. Muscle, organ and skeletal anatomy). The stifle joint connects the femur, which is the dog thigh bone, to the tibia and fibula, the lower leg bones, and the.
Femur of dog Anatomy of canine femur Anatomy of femur of dog Canine
The detailing of these structures changes based on dog breed due to the huge variation of size in dog breeds. In most dogs, it is slightly shorter than the tibia and the ulna and. A closer look at the anatomy. The stifle joint connects the femur, which is the dog thigh bone, to the tibia.
animal anatomy hip Google Search Leg Anatomy, Muscle Anatomy, Animal
Two of the most common are torn acls (ccls) and luxating patellas. The canine femur is the heaviest 4 and largest 5 canine bone. The distinction of the shape of the male and female pelvic inlet and outlet in humans is not made in dogs. The femur is a long (clyndircal) bone in the dog’s.
Femur Gross Anatomy Anjani Mishra
1 introduction to the femur: Two of the most common are torn acls (ccls) and luxating patellas. The largest bone in a dog’s body. The dog femur is the heaviest bone in the hindlimb. 3 common femur injuries in dogs: The stifle joint connects the femur, which is the dog thigh bone, to the tibia.
Canine Anatomy Veterian Key
The femur is a long (clyndircal) bone in the dog’s skeleton so that you will find all the typical osteological features. The largest bone in a dog’s body. 4 development and growth of. Two of the most common are torn acls (ccls) and luxating patellas. The stifle joint connects the femur, which is the dog.
Dog Femur OsteoID Bone Identification
The canine femur is the heaviest 4 and largest 5 canine bone. In most dogs, it is slightly shorter than the tibia and the ulna and. 4 development and growth of. The distinction of the shape of the male and female pelvic inlet and outlet in humans is not made in dogs. Muscle, organ and.
Femur Bones Dog Skeleton Anatomy for Medical Concept 3D Stock
The dog femur is the heaviest bone in the hindlimb. 2 structure and function of the femur: A closer look at the anatomy. Positional and directional terms, general terminology and anatomical orientation are. Muscle, organ and skeletal anatomy). You will find a nearly hemispherical head, neck, two processes, or trochanters at the proximal part of.
Dog Femur (Left) Head Greater trochanter Trochanteric fossa Neck
The femur is a long (clyndircal) bone in the dog’s skeleton so that you will find all the typical osteological features. A closer look at the anatomy. You will find a nearly hemispherical head, neck, two processes, or trochanters at the proximal part of the dog femur. Anatomy atlas of the canine general anatomy: The.
Veterinary Dog Anatomy InfoZone
The canine femur is the heaviest 4 and largest 5 canine bone. Muscle, organ and skeletal anatomy). Positional and directional terms, general terminology and anatomical orientation are. The dog femur is the heaviest bone in the hindlimb. 2 structure and function of the femur: 4 development and growth of. 3 common femur injuries in dogs:.
Dog Femur Anatomy 1 introduction to the femur: Muscle, organ and skeletal anatomy). In most dogs, it is slightly shorter than the tibia and the ulna and. A closer look at the anatomy. Fully labeled illustrations and diagrams of the dog (skeleton, bones, muscles, joints, viscera, respiratory system, cardiovascular system).
Anatomy Atlas Of The Canine General Anatomy:
4 development and growth of. The distinction of the shape of the male and female pelvic inlet and outlet in humans is not made in dogs. The femur is a long (clyndircal) bone in the dog’s skeleton so that you will find all the typical osteological features. 2 structure and function of the femur:
Muscle, Organ And Skeletal Anatomy).
Dog anatomy details the various structures of canines (e.g. The stifle joint connects the femur, which is the dog thigh bone, to the tibia and fibula, the lower leg bones, and the patella,the canine equivalent to the knee cap. A closer look at the anatomy. The dog femur is the heaviest bone in the hindlimb.
Fully Labeled Illustrations And Diagrams Of The Dog (Skeleton, Bones, Muscles, Joints, Viscera, Respiratory System, Cardiovascular System).
Positional and directional terms, general terminology and anatomical orientation are. In most dogs, it is slightly shorter than the tibia and the ulna and. The largest bone in a dog’s body. 1 introduction to the femur:
The Distal Portion Of The Dog Femur Is Quadrangular And Posses Condyles And Trochlea.
3 common femur injuries in dogs: The detailing of these structures changes based on dog breed due to the huge variation of size in dog breeds. The canine femur is the heaviest 4 and largest 5 canine bone. Two of the most common are torn acls (ccls) and luxating patellas.