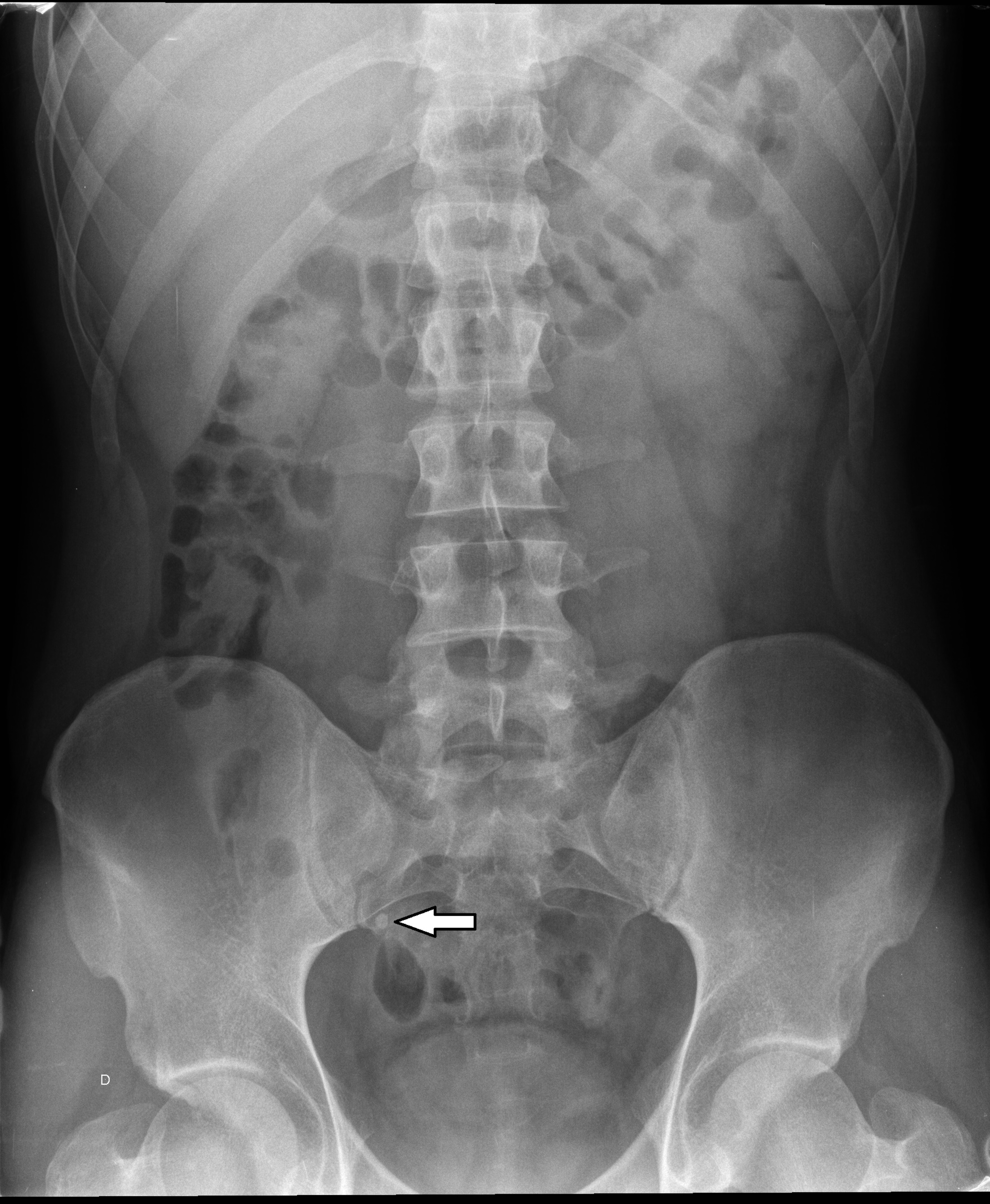
Abdomen X Ray Anatomy - Previous surgical history includes laparoscopic sterilization 12 months previously.
Abdomen X Ray Anatomy - Although abdominal radiography has lower sensitivity and specificity than a ct of the abdomen, it still serves a role as an adjunct or optional test. Evaluation of postprocedural free gas. These include an abdominal ct scan and renal or kidney tests. Evaluation of bowel gas in postoperative ileus. 27 public playlists include this case.
Moreover, it can help diagnose unexplained pain, nausea, or vomiting. It is used to evaluate the stomach, liver, intestines and spleen and may be used to help diagnose unexplained pain, nausea or vomiting. Negative study in some patients may obviate the need for ct. Previous surgical history includes laparoscopic sterilization 12 months previously. So left is right and vice versa. 27 public playlists include this case. Evaluation of radiopaque foreign bodies.
Introduction to Abdomen Radiography Radiology Key
It is sometimes abbreviated to axr, or kub (for kidneys, ureters, and urinary bladder). No rotation of shoulders or pelvis. Moreover, it can help diagnose unexplained pain, nausea, or vomiting. Radiographic anatomy of the chest and abdomen: It helps assess the stomach, intestines, liver, and sleep. Sterilization clips demonstrated in the pelvis. Stones in the.
Abdominal XRay Anatomy and Interpretation Checklist GrepMed
A preliminary evaluation of bowel gas in an emergent setting. In some circumstances an erect axr is requested: Stones in the gallbladder, kidneys, or ureters may be seen. Previous surgical history includes laparoscopic sterilization 12 months previously. An overview of abdominal radiographs, including indications, conventional views, normal anatomy, and common abnormalities (e.g. 27 public playlists.
Abdomen xray signs
The patient is standing, with ventral abdomen toward the image detector. Negative study in some patients may obviate the need for ct. In some circumstances an erect axr is requested: Evaluation of bowel gas in postoperative ileus. We’ve included the most routinely used radiographs. It helps assess the stomach, intestines, liver, and sleep. Field of.
X Ray Abdomen Anatomy Anatomical Charts & Posters
Field of view should span the inferior ribs to the inferior pubic rami, and include both lateral abdominal walls. In some circumstances an erect axr is requested: The patient is standing, with ventral abdomen toward the image detector. Evaluation of radiopaque lines and tubes. How the test is performed. Negative study in some patients may.
X Ray Abdomen Anatomy Anatomical Charts & Posters
Field of view should span the inferior ribs to the inferior pubic rami, and include both lateral abdominal walls. Evaluation of radiopaque lines and tubes. How the test is performed. In a normal axr, the contours of the psoas muscles are visible. A preliminary evaluation of bowel gas in an emergent setting. 27 public playlists.
Cureus Haemangiomas of the Small Intestine Poorly Known Cause of
Field of view should span the inferior ribs to the inferior pubic rami, and include both lateral abdominal walls. So left is right and vice versa. Previous surgical history includes laparoscopic sterilization 12 months previously. In a normal axr, the contours of the psoas muscles are visible. These include an abdominal ct scan and renal.
Image
We’ve included the most routinely used radiographs. 27 public playlists include this case. Sbo, ileus, volvulus, constipation, pneumoperitoneum,. Negative study in some patients may obviate the need for ct. Previous surgical history includes laparoscopic sterilization 12 months previously. So left is right and vice versa. How the test is performed. Examination that produces images of.
Pelvic X Ray Anatomy
The patient is standing, with ventral abdomen toward the image detector. Sbo, ileus, volvulus, constipation, pneumoperitoneum,. No rotation of shoulders or pelvis. Systematically review bowel gas, soft tissues, bones and abnormal calcification. A preliminary evaluation of bowel gas in an emergent setting. Organs include the liver, spleen, stomach, and intestines. Examine an axr as if.
Abdominal xray
Stones in the gallbladder, kidneys, or ureters may be seen. It helps assess the stomach, intestines, liver, and sleep. We’ve included the most routinely used radiographs. 27 public playlists include this case. Indications (acute) emergent evaluation of bowel gas. Sbo, ileus, volvulus, constipation, pneumoperitoneum,. Negative study in some patients may obviate the need for ct..
Approach to the Abdominal xray (AXR) Undergraduate Diagnostic
It is used to evaluate the stomach, liver, intestines and spleen and may be used to help diagnose unexplained pain, nausea or vomiting. No rotation of shoulders or pelvis. These include an abdominal ct scan and renal or kidney tests. Evaluation of postprocedural free gas. Moreover, it can help diagnose unexplained pain, nausea, or vomiting..
Abdomen X Ray Anatomy No rotation of shoulders or pelvis. How the test is performed. Field of view should span the inferior ribs to the inferior pubic rami, and include both lateral abdominal walls. We’ve included the most routinely used radiographs. Organs include the liver, spleen, stomach, and intestines.
Stones In The Gallbladder, Kidneys, Or Ureters May Be Seen.
Evaluation of bowel gas in postoperative ileus. Moreover, it can help diagnose unexplained pain, nausea, or vomiting. The standard abdominal radiograph (axr) taken is a supine projection: Indications (acute) emergent evaluation of bowel gas.
Generalized Abdominal Pain For 24 Hours And More Recent Onset Of Vomiting.
Evaluation of radiopaque lines and tubes. An overview of abdominal radiographs, including indications, conventional views, normal anatomy, and common abnormalities (e.g. Sbo, ileus, volvulus, constipation, pneumoperitoneum,. Field of view should span the inferior ribs to the inferior pubic rami, and include both lateral abdominal walls.
Although Abdominal Radiography Has Lower Sensitivity And Specificity Than A Ct Of The Abdomen, It Still Serves A Role As An Adjunct Or Optional Test.
Systematically review bowel gas, soft tissues, bones and abnormal calcification. It is used to evaluate the stomach, liver, intestines and spleen and may be used to help diagnose unexplained pain, nausea or vomiting. No rotation of shoulders or pelvis. A preliminary evaluation of bowel gas in an emergent setting.
What Are Some Common Uses Of The Procedure?
The patient is standing, with ventral abdomen toward the image detector. Uses for abdominal radiography include: The liver, kidneys, spleen and bladder can in some cases also be identified. It helps assess the stomach, intestines, liver, and sleep.